|
怎么把程序打包成 exe 文件 用 Setuptools 里的 py2exe 库 安装py2apppip3 install py2app
怎么把程序打包成 Mac 系统可运行的 .app 文件 cd 到Demo.py文件所在的目录 py2applet --make-setup Demo.py完成显示生成setup.py
怎么获取路径下所有目录名称?用 sys 下的 path 方法,返回的是目录名称的字符串列表 - >>> sys.path
- ['', '/Users/brucepk/Documents', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/3.7.3/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/python37.zip', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/3.7.3/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/python3.7', '/usr/local/Cellar/python/3.7.3/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/lib/python3.7/lib-dynload', '/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages']
用 os 模块下的 system 方法 - >>> os.system('cd /Users/brucepk/Desktop && mkdir aaa.txt')
- 256
用 time 模块里的 asctime 方法 - >>> import time
- >>> time.asctime()
- 'Sat Jul 4 17:36:00 2020'
用 time 模块里的 localtime 方法 - >>> import time
- >>> time.localtime(1888888888)
- time.struct_time(tm_year=2029, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=9, tm_hour=11, tm_min=21, tm_sec=28, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=313, tm_isdst=0)
用 time 模块里的 mktime 方法 - >>> time.mktime((2020, 7, 3, 21, 48, 56, 4, 21, 0))
- 1593784136.0
用 time 模块里的 strptime 方法 - >>> import time
- >>> time.strptime('Sun Jul 5 08:29:51 2020')
- time.struct_time(tm_year=2020, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=5, tm_hour=8, tm_min=29, tm_sec=51, tm_wday=6, tm_yday=187, tm_isdst=-1)
用 random 模块里的 shuffle 方法 - >>> import random
- >>> t = list(range(20))
- >>> t
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19]
- >>> random.shuffle(t)
- >>> t
- [16, 3, 13, 7, 6, 12, 17, 4, 15, 2, 5, 8, 18, 10, 9, 19, 14, 0, 1, 11]
- >>> st = '!@#$%^&*'
- >>> codes = []
- >>> for s in st:
- codes.append(ord(s))
- >>> codes
- [33, 64, 35, 36, 37, 94, 38, 42]
- >>> st = '!@#$%^&*'
- >>> codes = [ord(s) for s in st]
- >>> codes
- [33, 64, 35, 36, 37, 94, 38, 42]
很明显,用列表推导式实现比 for 循环加 append 更高效简洁,可读性更好。 打印出两个列表的笛卡尔积解法1:使用生成器表达式产生笛卡尔积,可以帮忙省掉运行 for 循环的开销。 - >>> colors = ['blacks', 'white']
- >>> sizes = ['S', 'M', 'L']
- >>> for tshirt in ('%s %s'%(c, s) for c in colors for s in sizes):
- print(tshirt)
- blacks S
- blacks M
- blacks L
- white S
- white M
- white L
- >>> import itertools
- >>> list(itertools.product(['blacks', 'white'], ['S', 'M', 'L']))
- [('blacks', 'S'), ('blacks', 'M'), ('blacks', 'L'), ('white', 'S'), ('white', 'M'), ('white', 'L')]
我们经常用 for 循环提取元组里的元素,对于我们不想接收的元素,我们可以用占位符 _ 接收。 - >>> player_infos = [('Kobe', '24'), ('James', '23'), ('Iverson', '3')]
- >>> for player_names, _ in player_infos:
- print(player_names)
- Kobe
- James
- Iverson
用 *args 的方式,*args 位置可以在任意位置。 - >>> a, b, *c = range(8)
- >>> a, b, c
- (0, 1, [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
- >>> a, *b, c, d = range(5)
- >>> a,b,c,d
- (0, [1, 2], 3, 4)
- >>> *a, b, c, d = range(5)
- >>> a,b,c,d
- ([0, 1], 2, 3, 4)
- >>> s = 'basketball'
- >>> s[::-1]
- 'llabteksab'
- >>> l = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> id(l)
- 4507638664
不会,可变序列用*=(就地乘法)后,不会创建新的序列,新元素追加到老元素上,以列表为例,我们看下新老列表的id,相等的。 - >>> l = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> id(l)
- 4507939272
- >>> l *= 2
- >>> l
- [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
- >>> id(l)
- 4507939272
会,不可变序列用*=(就地乘法)后,会创建新的序列,以元组为例,我们看下新老元组的id,是不同的。 - >>> t = (1, 2, 3)
- >>> id(t)
- 4507902240
- >>> t *= 2
- >>> t
- (1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3)
- >>> id(t)
- 4507632648
所以,对不可变序列进行重复拼接操作的话,效率会很低,因为每次都有一个新对象,而解释器需要把原来对象中的元素先复制到新的对象里,然后再追加新的元素。 关于+=的一道谜题- t = (1, 2, [30, 40])
- t[2] += [50, 60]
到底会发生下面4种情况中的哪一种? a. t变成(1, 2, [30, 40, 50, 60])。 b.因为tuple不支持对它的元素赋值,所以会抛出TypeError异常。 c.以上两个都不是。 d. a和b都是对的。 答案是d,请看下运行结果。 - >>> t = (1, 2, [30, 40])
- >>> t[2] += [50, 60]
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#1>", line 1, in <module>
- t[2] += [50, 60]
- TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
- >>> t
- (1, 2, [30, 40, 50, 60])
- l = [1, 9, 5, 8]
- j = l.sort()
- k = sorted(l)
通过 Python Tutor 工具我们可以看到,sort() 会就地在原序列上排序,sorted() 新建了一个新的序列。 list.sort方法会就地排序列表,也就是说不会把原列表复制一份。这也是这个方法的返回值是None的原因,提醒你本方法不会新建一个列表。在这种情况下返回None其实是Python的一个惯例:如果一个函数或者方法对对象进行的是就地改动,那它就应该返回None,好让调用者知道传入的参数发生了变动,而且并未产生新的对象。 怎么通过 reverse 参数对序列进行降序排列reverse 参数一般放在 sorted() 方法里面,reverse 默认值为 False,序列默认升序排列,降序排列的话需要将 reverse 值设置为 True。 - >>> l = [1, 9, 5, 8]
- >>> j = sorted(l, reverse=True)
- >>> j
- [9, 8, 5, 1]
- >>> a = numpy.arange(12)
- >>> a
- array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11])
- >>> a.shape = 3, 4
- >>> a
- array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
- [ 4, 5, 6, 7],
- [ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
可以通过切片指定位置插入,头部就是[0:0] - >>> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- >>> l[0:0] = 'Python'
- >>> l
- ['P', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- >>> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- >>> l.insert(0, 'first')
- >>> l
- ['first', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
在第一个元素之前添加一个元素之类的操作是很耗时的,因为这些操作会牵扯到移动列表里的所有元素。有没有更高效的方法?用双向队列 deque 类。 deque 类可以指定这个队列的大小,如果这个队列满员了,还可以从反向端删除过期的元素,然后在尾端添加新的元素。 - >>> from collections import deque
- >>> dp = deque(range(10), maxlen=15)
- >>> dp
- deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], maxlen=15)
- >>> dp.appendleft(-1)
- >>> dp
- deque([-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], maxlen=15)
Python中,你知道怎么创建字典吗? - a = dict(one=1, two=2, three=3)
- b = {'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3}
- c = dict(zip(['one', 'two', 'three'], [1, 2, 3]))
- d = dict([('two', 2), ('one', 1), ('three', 3)])
- e = dict({'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3})
- dial_code = [
- (86, 'China'),
- (91, 'India'),
- (1, 'US'),
- (55, 'Brazil'),
- (7, 'Russia'),
- (81, 'Japan')
- ]
- coutry_code = {coutry:code for code, coutry in dial_code}
用setdefault方法,只查询一次,效果更快 - coutry_code = {'China': 86, 'India': 91, 'US': 1, 'Brazil': 55, 'Russia': 7, 'Japan': 81}
- coutry_code.setdefault('china', []).append(86)
- if 'china' not in coutry_code:
- coutry_code['china'] = []
- coutry_code['china'].append(86)
- print(coutry_code)
像k in my_dict.keys( )这种操作在Python 3中是很快的,而且即便映射类型对象很庞大也没关系。这是因为dict.keys( )的返回值是一个“视图”。视图就像一个集合,而且跟字典类似的是,在视图里查找一个元素的速度很快。在“Dictionary view objects”里可以找到关于这个细节的文档。Python 2的dict.keys( )返回的是个列表,因此虽然上面的方法仍然是正确的,它在处理体积大的对象的时候效率不会太高,因为k in my_list操作需要扫描整个列表。 怎么统计字符串中元素出现的个数?用collections中的Counter方法统计,返回的结果是对应元素和个数形成的键值对。 - ct = collections.Counter('adcfadcfgbsdcv')
- Counter({'d': 3, 'c': 3, 'a': 2, 'f': 2, 'g': 1, 'b': 1, 's': 1, 'v': 1})
怎么统计出排名前n的元素? 用most_common方法,参数里填n,比如前两名的话 结果列表去重- >>> l = ['A', 'B', 'A', 'B']
- >>> list(set(l))
- ['A', 'B']
基础解法: - >>> m = {'A', 'B', 'C'}
- >>> n = {'B', 'C', 'D'}
- >>> found = 0
- >>> for i in m:
- if i in n:
- found += 1
-
- >>> found
- 2
- >>> m = {'A', 'B', 'C'}
- >>> n = {'B', 'C', 'D'}
- >>> len(m & n)
- 2
- >>> m = {'A', 'B', 'C'}
- >>> n = {'B', 'C', 'D'}
- >>> len(set(m) & srt(n))
- 2
- >>> m = {'A', 'B', 'C'}
- >>> n = {'B', 'C', 'D'}
- >>> len(set(m).intersection(n))
- 2
- >>> from unicodedata import name
- >>> {chr(i) for i in range(32, 256) if 'SIGN' in name(chr(i), '')}
- {'§', '%', '#', '+', '¬', '£', '<', '[b][font=STHeitiSC-Light][size=18px][b]查询系统默认编码方式[/b][/size][/font][/b][code]>>> fp = open('test.txt', 'w')
- >>> fp.encoding
- 'cp936'
- >>> fp = open('test.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
- >>> fp.encoding
- 'utf-8'
- def factorial(n):
- """:return n!"""
- return 1 if n < 2 else n * factorial(n-1)
用 Python 内置的函数 callable() 判断 - >>> [callable(obj) for obj in (abs, str, 2)]
- [True, True, False]
使用 dir 函数来获取对象的所有属性。 - >>> import requests
- >>> dir(requests)
- ['ConnectTimeout', 'ConnectionError', 'DependencyWarning', 'FileModeWarning', 'HTTPError', 'NullHandler', 'PreparedRequest', 'ReadTimeout', 'Request', 'RequestException', 'RequestsDependencyWarning', 'Response', 'Session', 'Timeout', 'TooManyRedirects', 'URLRequired', '__author__', '__author_email__', '__build__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__cake__', '__copyright__', '__description__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__license__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__path__', '__spec__', '__title__', '__url__', '__version__', '_check_cryptography', '_internal_utils', 'adapters', 'api', 'auth', 'certs', 'chardet', 'check_compatibility', 'codes', 'compat', 'cookies', 'cryptography_version', 'delete', 'exceptions', 'get', 'head', 'hooks', 'logging', 'models', 'options', 'packages', 'patch', 'post', 'put', 'pyopenssl', 'request', 'session', 'sessions', 'status_codes', 'structures', 'urllib3', 'utils', 'warnings']
创建一个空的用户定义的类和空的函数,计算差集,然后排序。 - >>> class C:
- pass
- >>> obj = C()
- >>> def func():
- pass
- >>> sorted(set(dir(func)) - set(dir(obj)))
- ['__annotations__', '__call__', '__closure__', '__code__', '__defaults__', '__get__', '__globals__', '__kwdefaults__', '__name__', '__qualname__']
那就要在关键字参数前加一个 *。 - >>> def f(a, *, b):
- return a, b
- >>> f(1, b=2)
- (1, 2)
这样的话,b 参数强制必须传入实参,否则会报错。 怎么给函数参数和返回值注解代码执行时,注解不会做任何处理,只是存储在函数的__annotations__属性(一个字典)中。 - def function(text: str, max_len: 'int > 0' = 80) -> str:
函数声明中的各个参数可以在:之后增加注解表达式。如果参数有默认值,注解放在参数名和=号之间。如果想注解返回值,在)和函数声明末尾的:之间添加->和一个表达式。 Python对注解所做的唯一的事情是,把它们存储在函数的__annotations__属性里。仅此而已,Python不做检查、不做强制、不做验证,什么操作都不做。换句话说,注解对Python解释器没有任何意义。注解只是元数据,可以供IDE、框架和装饰器等工具使用 不使用递归,怎么高效写出阶乘表达式通过 reduce 和 operator.mul 函数计算阶乘 - >>> from functools import reduce
- >>> from operator import mul
- >>> def fact(n):
- return reduce(mul, range(1, n+1))
- >>> fact(5)
函数装饰器在导入模块时立即执行,而被装饰的函数只在明确调用时运行。这突出了Python程序员所说的导入时和运行时之间的区别。 判断下面语句执行是否会报错?- >>> b = 3
- >>> def fun(a):
- print(a)
- print(b)
- b = 7
-
- >>> fun(2)
会报错,Python编译函数的定义体时,先做了一个判断,那就是 b 是局部变量,因为在函数中给它赋值了。但是执行 print(b) 时,往上又找不到 b 的局部值,所以会报错。 Python 设计如此,Python 不要求声明变量,但是假定在函数定义体中赋值的变量是局部变量。 - 2
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#50>", line 1, in <module>
- fun(2)
- File "<pyshell#49>", line 3, in fun
- print(b)
- UnboundLocalError: local variable 'b' referenced before assignment
用 global 声明 - >>> b = 3
- >>> def fun(a):
- global b
- print(a)
- print(b)
- b = 7
- >>> b = 5
- >>> fun(2)
- 2
- 5
我们知道,在闭包中,声明的变量是局部变量,局部变量改变的话会报错。 - >>> def make_averager():
- count = 0
- total = 0
- def averager (new_value):
- count += 1
- total += new_value
- return total / count
- return averager
- >>> avg = make_averager()
- >>> avg(10)
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#63>", line 1, in <module>
- avg(10)
- File "<pyshell#61>", line 5, in averager
- count += 1
- UnboundLocalError: local variable 'count' referenced before assignment
- >>> def make_averager():
- count = 0
- total = 0
- def averager (new_value):
- nonlocal count, total
- count += 1
- total += new_value
- return total / count
- return averager
- >>> avg = make_averager()
- >>> avg(10)
- 10.0
https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-3104/ 测试代码运行的时间用 time 模块里的 perf_counter 方法。 - >>> t0 = time.perf_counter()
- >>> for i in range(10000):
- pass
- >>> t1 = time.perf_counter()
- >>> t1-t0
- >>> import time
- >>> t0 = time.time()
- >>> for i in range(10000):
- pass
- >>> t1 = time.time()
- >>> t1-t0
怎么优化递归算法,减少执行时间使用装饰器 functools.lru_cache() 缓存数据 - >>> import functools
- >>> @functools.lru_cache()
- def fibonacci(n):
- if n < 2:
- return n
- return fibonacci(n-2)+fibonacci(n-1)
- >>> fibonacci(6)
- 8
用 == 运算符比较 - >>> a = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> b = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> a==b
- True
用 is 比较,ID一定是唯一的数值标注,而且在对象的生命周期中绝不会变 - >>> a = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> b = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> a is b
- False
可以用内置的 format( )函数和str.format( )方法。 format(my_obj, format_spec)的第二个参数,或者str.format( )方法的格式字符串,{}里代换字段中冒号后面的部分。 - >>> from datetime import datetime
- >>> now = datetime.now()
- >>> format(now, '%H:%M:%S')
- '08:18:21'
- >>> "It's now {:%I:%M%p}".format(now)
- "It's now 08:18AM"
可能有同学会想到用 pop(),但这个方法会就地删除原序列,不会复制出一个新的序列。 可以用切片的思想,比如复制后去掉后两个元素。 - >>> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- >>> j = l[:-2]
- >>> j
- [1, 2, 3]
在属性前加两个前导下划线,尾部没有或最多有一个下划线 怎么随机打乱一个列表里元素的顺序用 random 里的 shuffle 方法 - >>> from random import shuffle
- >>> l = list(range(30))
- >>> shuffle(l)
- >>> l
- [28, 15, 3, 25, 16, 18, 23, 10, 11, 21, 12, 7, 4, 0, 24, 6, 5, 22, 8, 13, 29, 9, 27, 17, 2, 20, 1, 26, 19, 14]
- >>>
用 Python 的内置函数 isinstance() 判读 - >>> isinstance('aa', str)
- True
用 fractions 中的 Fraction 方法 - >>> from fractions import Fraction
- >>> print(Fraction(1, 3))
- 1/3
- 两边必须是同类型的对象才能相加,+= 右操作数往往可以是任何可迭代对象。
- >>> l = list(range(6))
- >>> l += 'qwer'
- >>> l
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'q', 'w', 'e', 'r']
- >>> j = l + (6, 7)
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#91>", line 1, in <module>
- j = l + (6, 7)
- TypeError: can only concatenate list (not "tuple") to list
用 os.walk 生成器函数,我用 site-packages 目录举例。 - >>> import os
- >>> dirs = os.walk('C:\Program Files\Python36\Lib\site-packages')
- >>> for dir in dirs:
- print(dir)
-
- ('C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\Lib\\site-packages', ['ad3', 'ad3-2.2.1.dist-info', 'adodbapi', 'aip', 'appium', 'AppiumLibrary', 'Appium_Python_Client-0.46-py3.6.egg-info', 'apscheduler', 'APScheduler-3.6.0.dist-info', 'atomicwrites', 'atomicwrites-1.3.0.dist-info', ...)
高效的方法需要用到 itertools 和 operator 模块,导包后一行代码搞定。 - >>> import itertools
- >>> import operator
- >>> list(itertools.accumulate(range(1, 11), operator.mul))
- [1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880, 3628800]
用 itertools 里的 chain 方法可以一行代码搞定。 - >>> import itertools
- >>> list(itertools.chain('ABC', range(5)))
- ['A', 'B', 'C', 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
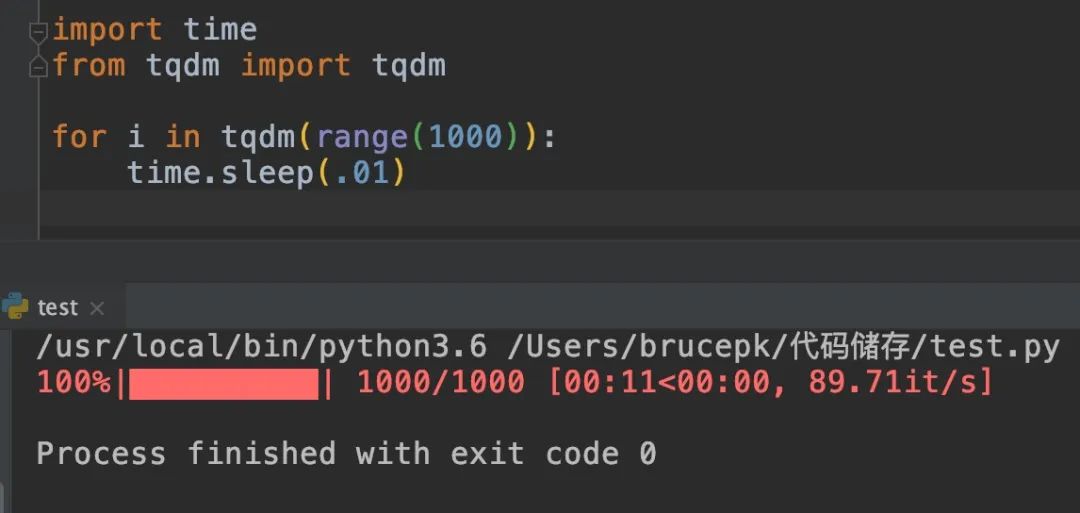
用 tqdm 库 - >>> import time
- >>> from tqdm import tqdm
- >>> for i in tqdm(range(1000)):
- time.sleep(.01)
-
- 0%| | 0/1000 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
- 1%| | 9/1000 [00:00<00:11, 88.38it/s]
- 2%|1 | 15/1000 [00:00<00:13, 74.85it/s]
- 2%|1 | 19/1000 [00:00<00:17, 56.93it/s]
- 2%|2 | 25/1000 [00:00<00:17, 56.70it/s]
- 3%|3 | 30/1000 [00:00<00:19, 50.90it/s
, '=', 'µ', '®', '÷', '©', '±', '°', '¤', '¥', '¶', '×', '>', '¢'}[/code]查询系统默认编码方式- >>> fp = open('test.txt', 'w')
- >>> fp.encoding
- 'cp936'
- >>> fp = open('test.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
- >>> fp.encoding
- 'utf-8'
- def factorial(n):
- """:return n!"""
- return 1 if n < 2 else n * factorial(n-1)
用 Python 内置的函数 callable() 判断 - >>> [callable(obj) for obj in (abs, str, 2)]
- [True, True, False]
使用 dir 函数来获取对象的所有属性。 - >>> import requests
- >>> dir(requests)
- ['ConnectTimeout', 'ConnectionError', 'DependencyWarning', 'FileModeWarning', 'HTTPError', 'NullHandler', 'PreparedRequest', 'ReadTimeout', 'Request', 'RequestException', 'RequestsDependencyWarning', 'Response', 'Session', 'Timeout', 'TooManyRedirects', 'URLRequired', '__author__', '__author_email__', '__build__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__cake__', '__copyright__', '__description__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__license__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__path__', '__spec__', '__title__', '__url__', '__version__', '_check_cryptography', '_internal_utils', 'adapters', 'api', 'auth', 'certs', 'chardet', 'check_compatibility', 'codes', 'compat', 'cookies', 'cryptography_version', 'delete', 'exceptions', 'get', 'head', 'hooks', 'logging', 'models', 'options', 'packages', 'patch', 'post', 'put', 'pyopenssl', 'request', 'session', 'sessions', 'status_codes', 'structures', 'urllib3', 'utils', 'warnings']
创建一个空的用户定义的类和空的函数,计算差集,然后排序。 - >>> class C:
- pass
- >>> obj = C()
- >>> def func():
- pass
- >>> sorted(set(dir(func)) - set(dir(obj)))
- ['__annotations__', '__call__', '__closure__', '__code__', '__defaults__', '__get__', '__globals__', '__kwdefaults__', '__name__', '__qualname__']
那就要在关键字参数前加一个 *。 - >>> def f(a, *, b):
- return a, b
- >>> f(1, b=2)
- (1, 2)
这样的话,b 参数强制必须传入实参,否则会报错。 怎么给函数参数和返回值注解代码执行时,注解不会做任何处理,只是存储在函数的__annotations__属性(一个字典)中。 - def function(text: str, max_len: 'int > 0' = 80) -> str:
函数声明中的各个参数可以在:之后增加注解表达式。如果参数有默认值,注解放在参数名和=号之间。如果想注解返回值,在)和函数声明末尾的:之间添加->和一个表达式。 Python对注解所做的唯一的事情是,把它们存储在函数的__annotations__属性里。仅此而已,Python不做检查、不做强制、不做验证,什么操作都不做。换句话说,注解对Python解释器没有任何意义。注解只是元数据,可以供IDE、框架和装饰器等工具使用 不使用递归,怎么高效写出阶乘表达式通过 reduce 和 operator.mul 函数计算阶乘 - >>> from functools import reduce
- >>> from operator import mul
- >>> def fact(n):
- return reduce(mul, range(1, n+1))
- >>> fact(5)
函数装饰器在导入模块时立即执行,而被装饰的函数只在明确调用时运行。这突出了Python程序员所说的导入时和运行时之间的区别。 判断下面语句执行是否会报错?- >>> b = 3
- >>> def fun(a):
- print(a)
- print(b)
- b = 7
-
- >>> fun(2)
会报错,Python编译函数的定义体时,先做了一个判断,那就是 b 是局部变量,因为在函数中给它赋值了。但是执行 print(b) 时,往上又找不到 b 的局部值,所以会报错。 Python 设计如此,Python 不要求声明变量,但是假定在函数定义体中赋值的变量是局部变量。 - 2
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#50>", line 1, in <module>
- fun(2)
- File "<pyshell#49>", line 3, in fun
- print(b)
- UnboundLocalError: local variable 'b' referenced before assignment
用 global 声明 - >>> b = 3
- >>> def fun(a):
- global b
- print(a)
- print(b)
- b = 7
- >>> b = 5
- >>> fun(2)
- 2
- 5
我们知道,在闭包中,声明的变量是局部变量,局部变量改变的话会报错。 - >>> def make_averager():
- count = 0
- total = 0
- def averager (new_value):
- count += 1
- total += new_value
- return total / count
- return averager
- >>> avg = make_averager()
- >>> avg(10)
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#63>", line 1, in <module>
- avg(10)
- File "<pyshell#61>", line 5, in averager
- count += 1
- UnboundLocalError: local variable 'count' referenced before assignment
- >>> def make_averager():
- count = 0
- total = 0
- def averager (new_value):
- nonlocal count, total
- count += 1
- total += new_value
- return total / count
- return averager
- >>> avg = make_averager()
- >>> avg(10)
- 10.0
https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-3104/ 测试代码运行的时间用 time 模块里的 perf_counter 方法。 - >>> t0 = time.perf_counter()
- >>> for i in range(10000):
- pass
- >>> t1 = time.perf_counter()
- >>> t1-t0
- >>> import time
- >>> t0 = time.time()
- >>> for i in range(10000):
- pass
- >>> t1 = time.time()
- >>> t1-t0
怎么优化递归算法,减少执行时间使用装饰器 functools.lru_cache() 缓存数据 - >>> import functools
- >>> @functools.lru_cache()
- def fibonacci(n):
- if n < 2:
- return n
- return fibonacci(n-2)+fibonacci(n-1)
- >>> fibonacci(6)
- 8
用 == 运算符比较 - >>> a = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> b = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> a==b
- True
用 is 比较,ID一定是唯一的数值标注,而且在对象的生命周期中绝不会变 - >>> a = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> b = [1, 2, 3]
- >>> a is b
- False
可以用内置的 format( )函数和str.format( )方法。 format(my_obj, format_spec)的第二个参数,或者str.format( )方法的格式字符串,{}里代换字段中冒号后面的部分。 - >>> from datetime import datetime
- >>> now = datetime.now()
- >>> format(now, '%H:%M:%S')
- '08:18:21'
- >>> "It's now {:%I:%M%p}".format(now)
- "It's now 08:18AM"
可能有同学会想到用 pop(),但这个方法会就地删除原序列,不会复制出一个新的序列。 可以用切片的思想,比如复制后去掉后两个元素。 - >>> l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- >>> j = l[:-2]
- >>> j
- [1, 2, 3]
在属性前加两个前导下划线,尾部没有或最多有一个下划线 怎么随机打乱一个列表里元素的顺序用 random 里的 shuffle 方法 - >>> from random import shuffle
- >>> l = list(range(30))
- >>> shuffle(l)
- >>> l
- [28, 15, 3, 25, 16, 18, 23, 10, 11, 21, 12, 7, 4, 0, 24, 6, 5, 22, 8, 13, 29, 9, 27, 17, 2, 20, 1, 26, 19, 14]
- >>>
用 Python 的内置函数 isinstance() 判读 - >>> isinstance('aa', str)
- True
用 fractions 中的 Fraction 方法 - >>> from fractions import Fraction
- >>> print(Fraction(1, 3))
- 1/3
- 两边必须是同类型的对象才能相加,+= 右操作数往往可以是任何可迭代对象。
- >>> l = list(range(6))
- >>> l += 'qwer'
- >>> l
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'q', 'w', 'e', 'r']
- >>> j = l + (6, 7)
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#91>", line 1, in <module>
- j = l + (6, 7)
- TypeError: can only concatenate list (not "tuple") to list
用 os.walk 生成器函数,我用 site-packages 目录举例。 - >>> import os
- >>> dirs = os.walk('C:\Program Files\Python36\Lib\site-packages')
- >>> for dir in dirs:
- print(dir)
-
- ('C:\\Program Files\\Python36\\Lib\\site-packages', ['ad3', 'ad3-2.2.1.dist-info', 'adodbapi', 'aip', 'appium', 'AppiumLibrary', 'Appium_Python_Client-0.46-py3.6.egg-info', 'apscheduler', 'APScheduler-3.6.0.dist-info', 'atomicwrites', 'atomicwrites-1.3.0.dist-info', ...)
高效的方法需要用到 itertools 和 operator 模块,导包后一行代码搞定。 - >>> import itertools
- >>> import operator
- >>> list(itertools.accumulate(range(1, 11), operator.mul))
- [1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040, 40320, 362880, 3628800]
用 itertools 里的 chain 方法可以一行代码搞定。 - >>> import itertools
- >>> list(itertools.chain('ABC', range(5)))
- ['A', 'B', 'C', 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
用 tqdm 库 - >>> import time
- >>> from tqdm import tqdm
- >>> for i in tqdm(range(1000)):
- time.sleep(.01)
-
- 0%| | 0/1000 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
- 1%| | 9/1000 [00:00<00:11, 88.38it/s]
- 2%|1 | 15/1000 [00:00<00:13, 74.85it/s]
- 2%|1 | 19/1000 [00:00<00:17, 56.93it/s]
- 2%|2 | 25/1000 [00:00<00:17, 56.70it/s]
- 3%|3 | 30/1000 [00:00<00:19, 50.90it/s
 
|